WHAT ARE KIDNEY STONES?
These stones consist of mineralized concretions from the kidneys.When calcium and uric acid crystallize and bond together stones begin to form.
In-organic calcium in the body causes buildup and formation of kidney stones.
Too much calcium can cause kidney stones and also may interfere with iron and zinc absorption.
Deficiency of calcium also leads to a higher risk of kidney stones.
See also Integumentary System - click here.
Kidney Function
The kidneys function as more than just a process to excrete nitrogenous waste. They conserve water and maintaining a water-salt balance and acid-base balance in the blood. This process is highly controlled by the kidneys in that it will pick and choose what is retained or excreted. The kidneys may excrete something as waste and in the next second they may retain it.The kidneys are primary organs of homeostasis. If the blood does not have the usual water-salt (electrolyte) balance, the blood volume and blood pressure are also affected.
Without adequate blood pressure, glomerular filtration in the kidneys and exchanges across the capillary walls cannot take place.
The body requires several minerals and trace minerals that are essential in the formation and processes of the cells and body fluids. The body contains more than 5 grams of each major mineral and less than 5 grams (about a teaspoon) for each trace mineral. The body also requires vitamins, but if the body gets the minerals it requires it can make most of the vitamins it needs.
Sodium regulates the body's water balance along with chloride. It is only recommended that a person takes in 500 mg of sodium daily. The average American consumes 4,000 mg or more of sodium daily. Magnesium is also important to the functioning of enzymes.
Most people are taking in too much or not enough of the amounts of minerals and trace minerals they need.
This can lead to mineral imbalances in the body and when there is an imbalance, the body is usually highly acidic which in turn sets the stage for disease and problems in the body such as kidney stones. If the body is alkaline there would be no pain and there would be no disease. Refer back to PH Balancing.
Kidney Stone Facts
- They are more common in young and middle-aged adults than in the elderly.
- They are much more prevalent in men than in women.
- They have also been known to form in children as young as 5 years of age.
- People living in hot climates also have an increased risk, mainly due to dehydration.
- Stones may very in color, but most are yellow or brown and they usually passed singly.
- Stones may be as small as or smaller than 0.1 mg which is relatively microscopic or have been seen as large as 1.36 Kilograms.
- Kidney Stones that are passed through the urine are very small usually 5mm or less.
- Stones that are of a medium size may travel through the kidneys into the ureter where they become lodged which causes urinary obstruction (a blockage in the flow of urine).
- Stones of a much larger diameter will remain in the kidney (nephrolithiasis) causing the urine flowing out of the kidney to be impared.
There are 4 common types of stones.
1) Struvite Stones- commonly associated with urinary tract infections. Specifically with the presence of bacteria that produce urea.
2) Cystine Stones- Rare and come from cystinuria (a genetic disorder most commonly a defect) from the transport of the amino acid cystine (a building block of protein). Cystine is known to precipitate from urine and form calculi (stones) in the urinary tract.
Cystein- A molecule composed of two Cystein amino acids joined by their sulfur atoms and is synthesized by the body from the essential amino acid methionine. This is also inherited by Parents or Grandparents. Ingestion of Protein allows Cystein to enter the body. Fish has a higher level of methionine and Cystein content. Also lowering sodium intake (table salt) is important.
Cystein becomes more soluble as ph increases. High levels of the cystine in urine result in formation of stones. The levels of cystine and urine play a major role in the rate at which
Stones form. Chronic cystine stones may lead to a very foul smell in the urine.
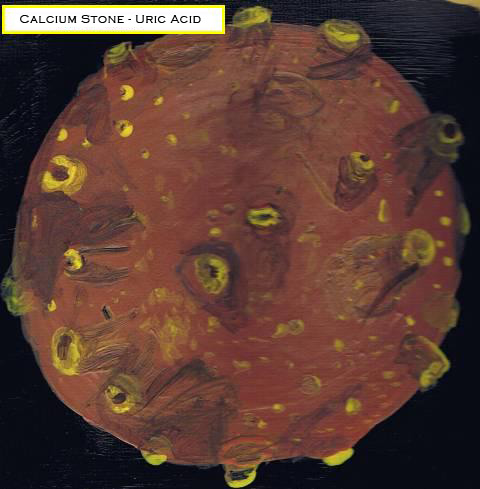
3) Calcium Stones- Uric acid-
Uric acid is developed by xanthine oxidase (an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxathine (a naturally occurring purine derivative) from xanthine (which further catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid) and hypoxathine, which is then produced from purine (an organic compound called heterocyclic aromatic). Uric acid is much more toxic to tissues and muscles than either xanthine or hypoxathine.
In humans, uric acid is the final process of oxidation (breakdown) process of purine metabolism excreted through urine. Uric acid is a strong reducer, and potent antioxidant. Also, it has more than half of the antioxidant capacity of blood. Blood plasma comes from uric acid. Also 70% of the daily uric acid to be disposed of is done through the kidneys.
Impaired disposal of uric acid by the kidneys, large amounts of fructose and foods that contain purine can be the result of elevated serum uric acid (hyperuicemia).
Levels of saturation through uric acid in the blood may result in the formation of kidney stones in which the urate crystallizes in the blood.
Uric acid stones are radiolucent and will not appear on an x-ray or CT scan. Uric acid stones are diagnosed by ultrasound. Only very large stones are detected through x-ray by the displacement of the surrounding kidney Increased acid (see PH levels) through digestion may lead to a higher production of endogenous acid in the liver and muscles which leads to an acid load increase on the kidneys. This increased load is handled poorly due to renal fat infiltration and insulin resistance which are felt to impair ammonia excretion (buffer).
When uric acid becomes insoluble, and crystallizes, stones form which also promotes calcium oxalate stones that act as "seed crystals" to form.
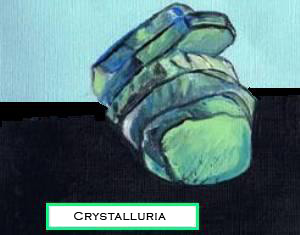
4) Calcium oxalate- crystal in the urine -
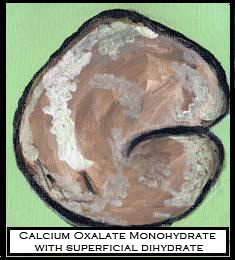
This is the most common form of kidney stones. May damage the kidneys permanently. There are three hydrated forms of calcium oxalate that occur naturally.
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate

Crystalluria
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate with superficial dihydrate